Abstract
Hyperleukocytic AML (HL-AML) is characterised by a high risk of early death and poor prognosis. We previously reported the impact of adding dexamethasone (DEX) to intensive chemotherapy in this situation (Bertoli et al, Haematologica 2018). The aim of this study was to give a comprehensive description of HL-AML at the molecular level and to investigate interactions between molecular lesions and DEX treatment.
In the earlier study which included 160 patients (pts) (18 - 75 years old) with WBC > 100 x 10 9/L or > 50 x 10 9/L with leukostasis symptoms, multivariate analyses had shown that DEX treatment was significantly associated with better DFS, EFS and OS (Bertoli S, Haematologica 2018). In this pre-midostaurin registration patient cohort (2004-2015), no pt received a FLT3 inhibitor. Diagnostic samples for NGS analyses were available for 154 pts (96.3% of the initial cohort), 59 pts who received DEX with 3+7 induction chemotherapy and 95 pts who did not. The presence of FLT3-ITD was tested as described (Larochelle O, Oncotarget 2011). CEBPA screening was performed by Sanger sequencing (Pabst T, Nat Genet 2001). Extended DNA resequencing was performed using an Illumina NextSeq500 and Sureselect target enrichment system (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA), targeted on the complete coding regions of 79 genes commonly mutated in myeloid malignancies.
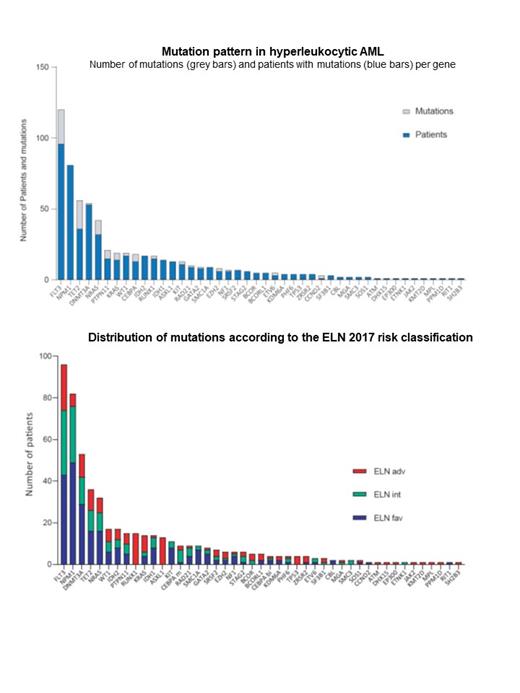
The cytogenetic risk was favorable, intermediate or adverse in 15 (9.7%), 121 (78.6%) and 18 (11.7%) pts. A total of 616 mutations were identified with an average of 4 mutations/pt (0 to 10 mutations/pt). Only one pt with inv(16) had no mutation detected. The most frequently mutated genes were FLT3 (62%), NPM1 (53%), DNMT3A (34%), TET2 (23%), NRAS (21%), IDH2 (12%), WT1 (11%), PTPN11 (10%), RUNX1 (10%), KRAS (9%) and IDH1 (9%). Of the 71 pts (46%) with FLT3-ITD mutations, 32 (45.1%) had an allelic ratio > 0.5. Mutations in the RAS pathway were detected in 67 pts (44%), including NRAS (n=32, 21%), PTPN11 (n=15, 10%), KRAS (n=14, 9%) and NF1 (n=6, 4%). Overall, a large majority of pts had mutations in signaling genes (n=131, 85.1%). Drug-actionable mutations such as FLT3 (n=96), IDH2 (n=17), IDH1 (n=14), KIT (n=11), TP53 (n=4) or JAK2 (n=1) were detected in 113 patients (73.4%). In patients with FLT3 mutations (n=96), 12 had co-mutations in IDH1 and 12 pts had co-mutations in IDH2.
The prognostic impact of the AML genomic classification (Papaemmanuil E, NEJM 2018), NPM1/FLT3-ITD/DNMT3A status, functional gene categories (Bullinger L, JCO 2017) ELN 2017 classification and individual genes was assessed. AML with inv(16)/CBFB-MYH11, CEBPA mutations, NPM1 mutations and myeloid transcription factor gene fusions or mutations were significantly and independently associated with better OS whereas the chromatin-modifying gene subset, NPM1/FLT3-ITD/DNMT3A triple mutations, ELN 2017-adverse risk and DNMT3A mutations were associated with poorer OS. NPM1/FLT3-ITD/DNMT3A triple mutations were observed in 25 pts (16%), 23 of whom died. Compared to this triple mutated subset, lower HRs were found in double mutant NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD (HR, 0.43; 95%CI: 0.19-0.97; P=0.041) or NPM1mut/DNMT3Amut (HR, 0.47; 95% CI: 0.21-1.07; P=0.074).
The prognostic impact of each individual gene was assessed using the LASSO statistical method. CBFB-MYH11 (HR, 0.10; 95% CI: 0.02-0.43; P=0.002), CEBPA (HR, 0.22; 95% CI: 0.09-0.53; P=0.001), NPM1 (HR, 0.33; 95% CI: 0.19-0.58; P<0.001) and surprisingly, RUNX1 mutations (HR, 0.40; 95% CI: 0.18-0.92; P=0.030) were independently associated with better OS. DNMT3A mutations were independently predictive of poor OS (HR, 1.76; 95% CI: 1.02-3.03; P=0.043).
Median DFS (13.6 months vs 66.3, P=0.002), EFS (11.3 vs 39.4, P=0.002) and OS (18.3 vs not reached, P=0.006) were significantly better in pts who received DEX. In multivariate analyses, no significant interaction between DEX and classifications or gene mutations was found, indicating that the effect of DEX did not differ significantly between the various genetic subsets. This may be due to insufficient numbers or DEX may have broader effects on biological phenomena such as inflammation.
Since more than 80% of pts have mutations in signaling genes, inhibition of signaling pathways could improve prognosis of HL-AML. The impact of midostaurin will be interesting to analyse in this setting. Inhibition of the RAS pathway could also be a valuable avenue.
Bertoli: Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Tavitian: Novartis: Consultancy. Vergez: Pierre Fabre Laboratory: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding. Huguet: Novartis: Other: Advisor; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Advisor; Celgene: Other: Advisor; BMS: Other: Advisor; Amgen: Other: Advisor; Pfizer: Other: Advisor. Delabesse: Novartis: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy. Recher: Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MaatPharma: Research Funding; Macrogenics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
dexamethasone in hyperleukocytic AML.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal